
In collaboration with Analia Zwick and Gonzalo Alvarez, Bariloche Atomic Center, Argentina
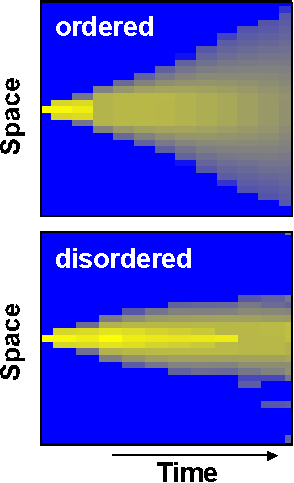 Most physical realisations of quantum computers that have been suggested to date cannot be realised with current technology. The major exception is nulcear magnetic resonance. We use liquid-state NMR to implement various quantum algorithms and to simulate quantum systems on an NMR quantum computer. This system allows very precise control of the evolution of the quantum system and a large amount of fleibility in choosing the quantum system that is best suited for a given task. In addition, we also use solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance. The dipolar couplings that are present in these systems allow one to combine many spins into a quantum register with several thousand qubits. Using this system, we could show that quantum mechanical superposition states decay at a rate that increases with the square root of the number of qubits in the system. Furthermore, it turned out to be possible to reduce the decoherence rate by modulating the system-environment interaction in a suitable way. This allowed us to reduce the decoherence rate by almost two orders of magnitude. Solid-state NMR also allows us to simulate quantum systems. As an example, the figures on the right hand side show the effect of disorder on the spreading of information: Starting from individual spins, an appropriate Hamiltonian can spread quantum information to arbitrarily large systems, as shown in the experimental data in the upper panel. With increasing perturbation, this spreading stops and we observe a quasi-equilibrium of the system (see lower panel). The size of this stationary state (in terms of spatial extent or number of correlated spins) decreases with the strength of the perturbation. The result can be described as a localization-delocalization phase transition.
Most physical realisations of quantum computers that have been suggested to date cannot be realised with current technology. The major exception is nulcear magnetic resonance. We use liquid-state NMR to implement various quantum algorithms and to simulate quantum systems on an NMR quantum computer. This system allows very precise control of the evolution of the quantum system and a large amount of fleibility in choosing the quantum system that is best suited for a given task. In addition, we also use solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance. The dipolar couplings that are present in these systems allow one to combine many spins into a quantum register with several thousand qubits. Using this system, we could show that quantum mechanical superposition states decay at a rate that increases with the square root of the number of qubits in the system. Furthermore, it turned out to be possible to reduce the decoherence rate by modulating the system-environment interaction in a suitable way. This allowed us to reduce the decoherence rate by almost two orders of magnitude. Solid-state NMR also allows us to simulate quantum systems. As an example, the figures on the right hand side show the effect of disorder on the spreading of information: Starting from individual spins, an appropriate Hamiltonian can spread quantum information to arbitrarily large systems, as shown in the experimental data in the upper panel. With increasing perturbation, this spreading stops and we observe a quasi-equilibrium of the system (see lower panel). The size of this stationary state (in terms of spatial extent or number of correlated spins) decreases with the strength of the perturbation. The result can be described as a localization-delocalization phase transition.
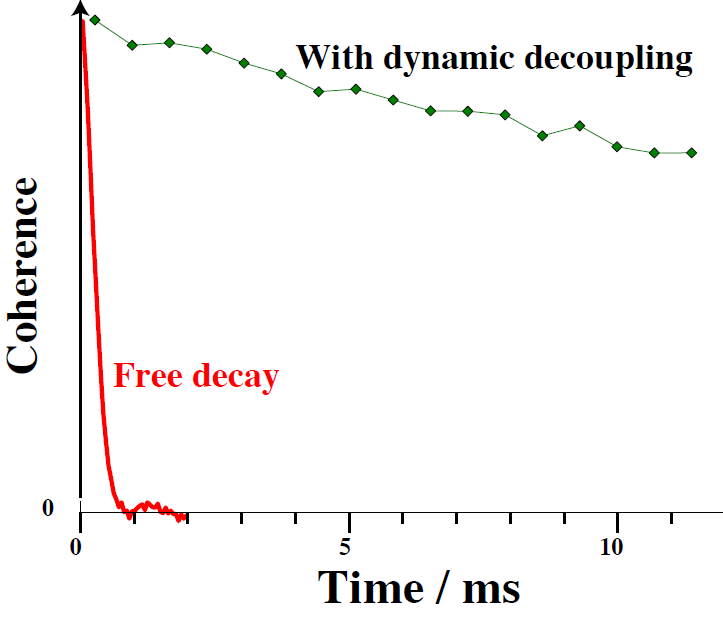 The scientific community is currently exploring many different physical implementations of quantum information processing. The main common feature of all these implementations is that the lifetime of the quantum information is too short to allow large-scale computation. The decay of the quantum states arises from the unavoidable interaction between the quantum system and its environment. A possible remedy for this issue consists in applying sequences of pi-rotations to the qubits, which are designed to make the interaction between system and environment time-dependent, such that its average value vanishes. We have experimentally compared several proposed sequences, using a simple quantum computer based on nuclear spins. We could show that the concept works and that it allows one to extend the lifetime of qubits by many orders of magnitude. We could also show that for practical implementations, the imperfections of experimentally possible rotations can cause more damage than the environment. We therefore designed sequences of rotations around different axes where the pulse imperfections do not add over the sequence, but actually cancel. The resulting sequences are thus robust against imperfections and provide optimal decoupling over a wide range of parameters.
The scientific community is currently exploring many different physical implementations of quantum information processing. The main common feature of all these implementations is that the lifetime of the quantum information is too short to allow large-scale computation. The decay of the quantum states arises from the unavoidable interaction between the quantum system and its environment. A possible remedy for this issue consists in applying sequences of pi-rotations to the qubits, which are designed to make the interaction between system and environment time-dependent, such that its average value vanishes. We have experimentally compared several proposed sequences, using a simple quantum computer based on nuclear spins. We could show that the concept works and that it allows one to extend the lifetime of qubits by many orders of magnitude. We could also show that for practical implementations, the imperfections of experimentally possible rotations can cause more damage than the environment. We therefore designed sequences of rotations around different axes where the pulse imperfections do not add over the sequence, but actually cancel. The resulting sequences are thus robust against imperfections and provide optimal decoupling over a wide range of parameters.
Jingfu Zhang
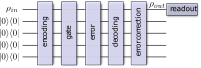 Large-scale universal quantum computing requires a mechanism for the elimination of errors, which arise from unwanted interactions with the environment as well as from the finite precision of experimentally realizable control operations. Quantum error correction (QEC) achieves this in a similar way as classical error correction: the information of a logical qubit is encoded in multiple physical qubits. At regular intervals, the system state is checked for possible errors and they are corrected. We have implemented an error correction code that is able to correct all possible single-qubit errors and combined this protection scheme with logical gate operations on the encoded qubit. The experimental data show that this scheme increases the overall fidelity of the gate operations.
Large-scale universal quantum computing requires a mechanism for the elimination of errors, which arise from unwanted interactions with the environment as well as from the finite precision of experimentally realizable control operations. Quantum error correction (QEC) achieves this in a similar way as classical error correction: the information of a logical qubit is encoded in multiple physical qubits. At regular intervals, the system state is checked for possible errors and they are corrected. We have implemented an error correction code that is able to correct all possible single-qubit errors and combined this protection scheme with logical gate operations on the encoded qubit. The experimental data show that this scheme increases the overall fidelity of the gate operations.
Jingfu Zhang
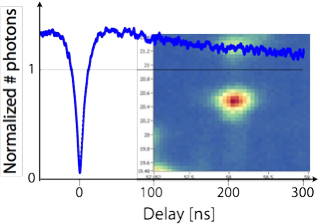 The nitrogen-vacancy (NV)-center of diamond has almost ideal properties for testing basic concepts of quantum information processing on single particles (electron- and nuclear spins). We design quantum gate operations and test dynamical decoupling schemes, which extend the coherence time of the electron spin almost to the T1-limit (~4 ms). Combining the electron spin with the nuclear spin degrees of freedom of nitrogen (14N) and carbon (13C) nuclei allows one to implement simple quantum computing devices with 2-5 qubits.
The nitrogen-vacancy (NV)-center of diamond has almost ideal properties for testing basic concepts of quantum information processing on single particles (electron- and nuclear spins). We design quantum gate operations and test dynamical decoupling schemes, which extend the coherence time of the electron spin almost to the T1-limit (~4 ms). Combining the electron spin with the nuclear spin degrees of freedom of nitrogen (14N) and carbon (13C) nuclei allows one to implement simple quantum computing devices with 2-5 qubits.
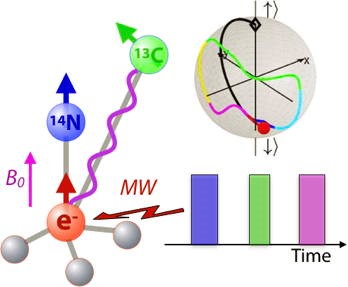
A single electronic spin in nitrogen-vacancy (NV)-center of diamond can be coupled to tens of 13C nuclear spins, making the system a potential candidate for scalable quantum information processors. However, the control of the weakly coupled nuclear spins is very inefficient with conventional approaches based on radio-frequency pulses. Here, we efficiently control the individual nuclear spins by indirect control where we only apply microwave (MW) pulses on the electron spin. These pulses change the state of the electron spin and thereby also the effective quantization axis of the nuclear spin, which is given by the Zeeman field plus the hyperfine interaction. Combined with free evolution during the delays between the microwave pulses, this approach allows us to generate arbitrary gate operations and achieve universal control of the quantum register. Using only 2-3 pulses and delays, we demonstrated state initialization, gate operations and readout. The experiments were implemented on a weakly coupled 13C spin, with a hyperfine coupling about 3 orders of magnitude smaller than the nearest neighbour 13C spin. Details are given in this paper. The figure shows a schematic picture of an NV center coupled to a 13C spin, the MW pulse sequence the trajectory of the 13C spin on the Bloch sphere during a CNOT operation. We are currently extending this approach to the implementation of full quantum algorithms.
[1] Scalable architecture for spin-based quantum computers with a single type of gate
D. Suter and K. Lim
Phys. Rev. A 65, 052309 (2002)
[2] Scaling of Decoherence in Wide NMR Quantum Registers
H. G. Krojanski and D. Suter
Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 090501 (2004)
[3] Quantum phase transition of ground-state entanglement in a Heisenberg spin chain simulated in an NMR quantum computer
X. Peng, J. Du and D. Suter
Phys. Rev. A 71, 012307 (2005)
[4] Quantum and classical parallelism in parity algorithms for ensemble quantum computers
R. Stadelhofer, D. Suter and W. Banzhaf
Phys. Rev. A 71, 032345 (2005)
[5] Quantification of complementarity in multiqubit systems
X. Peng, X. Zhu, D. Suter, J. Du, M. Liu and K. Gao
Phys. Rev. A 72, 052109 (2005)
[6] Speedup of quantum-state transfer by three-qubit interactions: Implementation by nuclear magnetic resonance
J. Zhang, X. Peng and D. Suter
Phys. Rev. A 73, 062325 (2006)
[7] Reduced Decoherence in Large Quantum Registers
H. G. Krojanski and D. Suter
Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 150503 (2006)
[8] Quantum-information processing using strongly dipolar coupled nuclear spins
T. S. Mahesh and D. Suter
Phys. Rev. A 74, 062312 (2006)
[9] Decoherence in large NMR quantum registers
H. G. Krojanski and D. Suter
Phys. Rev. A 74, 062319 (2006)
[10] Experimental realization of 1->2 asymmetric phase-covariant quantum cloning
H. Chen, X. Zhou, D. Suter and J. Du
Phys. Rev. A 75, 012317 (2007)
[11] Two-qubit gates between noninteracting qubits in endohedral-fullerene-based quantum computation
C. Ju, D. Suter and J. Du
Phys. Rev. A 75, 012318 (2007)
[12] Decoherence in large quantum registers under variable interaction with the environment
M. Lovric, H. G. Krojanski and D. Suter
Phys. Rev. A 75, 042305 (2007)
[13] Effect of system level structure and spectral distribution of the environment on the decoherence rate
J. Zhang, X. Peng, N. Rajendran and D. Suter
Phys. Rev. A 75, 042314 (2007)
[14] Iterative quantum-state transfer along a chain of nuclear spin qubits
J. Zhang, N. Rajendran, X. Peng and D. Suter
Phys. Rev. A 76, 012317 (2007)
[15] Measuring complete quantum states with a single observable
X. Peng, J. Du and D. Suter
Phys. Rev. A 76, 042117 (2007)
[16] Experimental observation of a topological phase in the maximally entangled state of a pair of qubits
J. Du, J. Zhu, M. Shi, X. Peng and D. Suter
Phys. Rev. A 76, 042121 (2007)
[17] Quantum Computing: A Short Course from Theory to Experiment
J. Stolze and D. Suter
Wiley-VCH, Berlin (2008)
ISBN ISBN 978-3-527-40787-3
[18] Spins as qubits: Quantum information processing by nuclear magnetic resonance
D. Suter and T. S. Mahesh
J. Chem. Phys. 128, 052206 (2008)
[19] Detection of Quantum Critical Points by a Probe Qubit
J. Zhang, X. Peng, N. Rajendran and D. Suter
Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 100501 (2008)
[20] Quantitative complementarity between local and nonlocal character of quantum states in a three-qubit system
X. Peng, J. Zhang, J. Du and D. Suter
Phys. Rev. A 77, 052107 (2008)
[21] Evolving blackbox quantum algorithms using genetic programming
R. Stadelhofer, W. Banzhaf and D. Suter
AI EDAM 22, 285-297 (2008)
[22] NMR implementation of factoring large numbers with Gauß sums: Suppression of ghost factors
X. Peng and D. Suter
Europhys. Lett. 84, 40006 (5pp) (2008)
[23] Quantum Adiabatic Algorithm for Factorization and Its Experimental Implementation
X. Peng, Z. Liao, N. Xu, G. Qin, X. Zhou, D. Suter and J. Du
Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 220405 (2008)
[24] Nuclear spin qubits in a trapped-ion quantum computer
M. Feng, Y. Y. Xu, F. Zhou and D. Suter
Phys. Rev. A 79, 052331 (2009)
[25] Quantum Simulation of a System with Competing Two- and Three-Body Interactions
X. Peng, J. Zhang, J. Du and D. Suter
Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 140501 (2009)
[26] Spin qubits for quantum simulations
X. Peng and D. Suter
Frontiers of Physics in China 5, 1-25 (2010)
[27] Quantum-information-processing architecture with endohedral fullerenes in a carbon nanotube
W. L. Yang, Z. Y. Xu, H. Wei, M. Feng and D. Suter
Phys. Rev. A 81, 032303 (2010)
[28] Experimental generation of pseudo-bound-entanglement
H. Kampermann, D. Bruß, X. Peng and D. Suter
Phys. Rev. A 81, 040304 (2010)
[29] Ground-state entanglement in a system with many-body interactions
X. Peng, J. Zhang, J. Du and D. Suter
Phys. Rev. A 81, 042327 (2010)
[30] NMR Quantum Simulation of Localization Effects Induced by Decoherence
G. A. Álvarez and D. Suter
Phys. Rev. Lett. 104, 230403 (2010)
[31] Liquid-State NMR Quantum Computing
L. M. K. Vandersypen, I. L. Chuang and D. Suter
Editors: D. M. Grant and R. K. Harris
John Wiley & Sons, Chichester (2010)
[32] Performance comparison of dynamical decoupling sequences for a qubit in a rapidly fluctuating spin bath
G. A. Álvarez, A. Ajoy, X. Peng and D. Suter
Phys. Rev. A 82, 042306 (2010)
[33] Observation of the Ground-State Geometric Phase in a Heisenberg XY Model
X. Peng, S. Wu, J. Li, D. Suter and J. Du
Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 240405 (2010)
[34] An endohedral fullerene-based nuclear spin quantum computer
C. Ju, D. Suter and J. Du
Physics Letters A 375, 1441 - 1444 (2011)
[35] Optimal pulse spacing for dynamical decoupling in the presence of a purely dephasing spin bath
A. Ajoy, G. A. Álvarez and D. Suter
Phys. Rev. A 83, 032303 (2011)
[36] Experimental demonstration of a unified framework for mixed-state geometric phases
J. Zhu, M. Shi, V. Vedral, X. Peng, D. Suter and J. Du
EuroPhys. Lett. 94, 20007 (2011)
[37] Robust Dynamical Decoupling for Quantum Computing and Quantum Memory
A. M. Souza, G. A. Álvarez and D. Suter
Phys. Rev. Lett. 106, 240501 (2011)
[38] Localization effects induced by decoherence in superpositions of many-spin quantum states
G. A. Álvarez and D. Suter
Phys. Rev. A 84, 012320 (2011)
[39] High fidelity quantum memory via dynamical decoupling: theory and experiment
X. Peng, D. Suter and D. A. Lidar
J. Phys. B 44, 154003 (2011)
[40] Measuring the Spectrum of Colored Noise by Dynamical Decoupling
G. A. Álvarez and D. Suter
Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 230501 (2011)
[41] An Efficient Exact Quantum Algorithm for the Integer Square-free Decomposition Problem
J. Li, X. Peng, J. Du and D. Suter
Sci. Rep. 2, 260 (2012)
[42] Effects of time-reversal symmetry in dynamical decoupling
A. M. Souza, G. A. Álvarez and D. Suter
Phys. Rev. A 85, 032306 (2012)
[43] Iterative rotation scheme for robust dynamical decoupling
G. A. Álvarez, A. M. Souza and D. Suter
Phys. Rev. A 85, 052324 (2012)
[44] Robust dynamical decoupling for arbitrary quantum states of a single NV center in diamond
J. H. Shim, I. Niemeyer, J. Zhang and D. Suter
EPL (Europhysics Letters) 99, 40004 (2012)
[45] Robust dynamical decoupling
A. M. Souza, G. A. Álvarezz and D. Suter
Phil. Trans. Royal Soc. A 370, 4748-4769 (2012)
[46] Experimental Implementation of Encoded Logical Qubit Operations in a Perfect Quantum Error Correcting Code
J. Zhang, R. Laflamme and D. Suter
Phys. Rev. Lett. 109, 100503 (2012)
[47] Experimental protection of quantum gates against decoherence and control errors
A. M. Souza, G. A. Álvarez and D. Suter
Phys. Rev. A 86, 050301 (2012)
[48] Room-temperature high-speed nuclear-spin quantum memory in diamond
J. H. Shim, I. Niemeyer, J. Zhang and D. Suter
Phys. Rev. A 87, 012301 (2013)
[49] Robustness of dynamical decoupling sequences
M. A. Ali Ahmed, G. A. Álvarez and D. Suter
Phys. Rev. A 87, 042309 (2013)
[50] Experimental Implementation of Assisted Quantum Adiabatic Passage in a Single Spin
J. Zhang, J. H. Shim, I. Niemeyer, T. Taniguchi, T. Teraji, H. Abe, S. Onoda, T. Yamamoto, T. Ohshima, J. Isoya and D. Suter
Phys. Rev. Lett. 110, 240501 (2013)
[51] Quantum simulations of localization effects with dipolar interactions
G. A. Álvarez, R. Kaiser and D. Suter
Annalen der Physik 525, 833--844 (2013)
[52] Protected Quantum Computing: Interleaving Gate Operations with Dynamical Decoupling Sequences
J. Zhang, A. M. Souza, F. D. Brandao and D. Suter
Phys. Rev. Lett. 112, 050502 (2014)
[53] Experimental Implementation of Adiabatic Passage between Different Topological Orders
X. Peng, Z. Luo, W. Zheng, S. Kou, D. Suter and J. Du
Phys. Rev. Lett. 113, 080404 (2014)
[54] Construction of arbitrary robust one-qubit operations using planar geometry
T. Ichikawa, J. G. Filgueiras, M. Bando, Y. Kondo, M. Nakahara and D. Suter
Phys. Rev. A 90, 052330 (2014)
[55] Experimental implementation of quantum gates through actuator qubits
J. Zhang, D. Burgarth, R. Laflamme and D. Suter
Phys. Rev. A 91, 012330 (2015)
[56] Hybrid magic state distillation for universal fault-tolerant quantum computation
W. Zheng, Y. Yu, J. Pan, J. Zhang, J. Li, Z. Li, D. Suter, X. Zhou, X. Peng and J. Du
Phys. Rev. A 91, 022314 (2015)
[57] Localization-delocalization transition in the dynamics of dipolar-coupled nuclear spins
G. A. Álvarez, D. Suter and R. Kaiser
Science 349, 846-848 (2015)
[58] Experimental Protection of Two-Qubit Quantum Gates against Environmental Noise by Dynamical Decoupling
J. Zhang and D. Suter
Phys. Rev. Lett. 115, 110502 (2015)
[59] High-fidelity gate operations for quantum computing beyond dephasing time limits
A. M. Souza, R. S. Sarthour, I. S. Oliveira and D. Suter
Phys. Rev. A 92, 062332 (2015)
[60] Characterization of hyperfine interaction between an NV electron spin and a first-shell 13C nuclear spin in diamond
K. R. K. Rao and D. Suter
Phys. Rev. B 94, 060101 (2016)
[61] Colloquium : Protecting quantum information against environmental noise
D. Suter and G. A. Alvarez
Rev. Mod. Phys. 88, 041001 (Oct.2016)
[62] Defect production in non-equilibrium phase transitions: experimental investigation of the Kibble-Zurek mechanism in a two-qubit quantum simulator
J. Zhang, F. M. Cucchietti, R. Laflamme and D. Suter
New Journal of Physics 19, 043001 (2017)
[63] Quantum Image Processing and Its Application to Edge Detection: Theory and Experiment
X. Yao, H. Wang, Z. Liao, M. Chen, J. Pan, J. Li, K. Zhang, X. Lin, Z. Wang, Z. Luo, W. Zheng, J. Li, M. Zhao, X. Peng and D. Suter
Phys. Rev. X 7, 031041 (2017)
[64] Superposing pure quantum states with partial prior information
S. Dogra, G. Thomas, S. Ghosh and D. Suter
Phys. Rev. A 97, 052330 (2018)
[65] Pulse sequences for controlled two- and three-qubit gates in a hybrid quantum register
J. Zhang, S. S. Hegde and D. Suter
Phys. Rev. A 98, 042302 (2018)
[66] Bloch-Siegert shift in a hybrid quantum register: Quantification and compensation
J. Zhang, S. Saha and D. Suter
Phys. Rev. A 98, 052354 (2018)
[67] Floquet engineering to entanglement protection of distant nitrogen vacancy centers
W. L. Yang, W. L. Song, J. An, M. Feng, D. Suter and J. Du
New J. Phys. 21, 013007 (2019)
[68] Improved Indirect Control of Nuclear Spins in Diamond N-$V$ Centers
J. Zhang, S. S. Hegde and D. Suter
Phys. Rev. Applied 12, 064047 (2019)
[69] Efficient Quantum Gates for Individual Nuclear Spin Qubits by Indirect Control
S. S. Hegde, J. Zhang and D. Suter
Phys. Rev. Lett. 124, 220501 (2020)
[70] Efficient Implementation of a Quantum Algorithm in a Single Nitrogen-Vacancy Center of Diamond
J. Zhang, S. S. Hegde and D. Suter
Phys. Rev. Lett. 125, 030501 (2020)
[71] Decoherence scaling transition in the dynamics of quantum information scrambling
F. D. Domínguez, M. C. Rodríguez, R. Kaiser, D. Suter and G. A. Álvarez
Phys. Rev. A 104, 012402 (2021)
[72] Optimization of a quantum control sequence for initializing a nitrogen-vacancy spin register
T. Chakraborty, J. Zhang and D. Suter
Phys. Rev. A 105, 022622 (2022)
[73] Toward the Speed Limit of High-Fidelity Two-Qubit Gates
S. S. Hegde, J. Zhang and D. Suter
Phys. Rev. Lett. 128, 230502 (2022)